
Typically, below the age of 12 or so, students are far better at seeing the world in concrete terms than they are at understanding abstractions. Visual approach to help younger students with abstract conceptsĪnother challenge word problems present is that they often challenge students to reason or think through problems abstractly. In addition, as they get more experience at drawing out these diagrams, they can get better at organizing and presenting that information in a meaningful and more organized way, something that’s helpful for students who have a hard time showing their work or communicating their thoughts succinctly or mathematically. In order to build a strip diagram, students need to parse out the important information, collecting information on:Īs a student gets more practice in building strip diagrams, they can become more adept at highlighting key information, ignoring irrelevant information, and identifying key math terms as hints for what the operation is supposed to be about.
Strip diagrams can help by providing students with a ready and systematic method of approaching these problems. Rather than being presented with a straight forward math problem, students are suddenly faced with a paragraph of words and numbers.įrom this jumble of words, they have to keep track of a lot of different information, figure out what’s important, determine what the question actually is (since it’s usually cloaked in specific math vocabulary) and, finally, they have to figure out what to do. Younger students often struggle with word problems for a variety of reasons.įor one thing, word problems (unlike computational exercises) involve much more than math. Why Some Curricula Use Strip Diagrams A systematic approach to confusing word problems
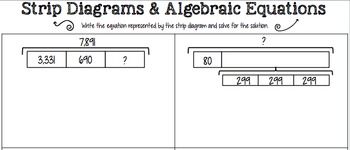
In essence, a large rectangle is placed at the top, representing a whole amount.īelow it, a same-sized rectangle is divided up into two or more pieces, representing the different parts that can make up that whole.ĭepending on the problem, these can be uneven in size (representing two different numbers – such as in an addition or subtraction) or equal in size.Ī bar might even be broken down into several, separate parts, as might be found in multiplication and division. Generally speaking, the first strip diagram most students will learn is the part-part whole model. In general, there are a few different ways that parents and teachers use strip diagrams to solve different math problems. Different types of strip diagram strategies
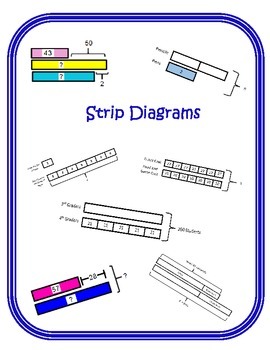
The overarching principle is that, by drawing out a model, students learn to pick out the different variables given in a word problem, what they need to find and can then figure out what operation and methods they need to use to solve the problem in question. Typically, strip diagrams are used as a tool to help students visualize problems and what operations they’re being asked to do (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division), something that can be particularly helpful with word problems. Strip diagrams are actually pretty flexible visual tools that can be used when learning different topics and when confronted by different types of word problems. The overall idea is that with a drawing or picture students can better visualize a problem and then decide what operation they should use to get the answer. A strip diagram, sometimes known as a bar model, length model or fraction strip, is a kind of visual model used when teaching math in order to demonstrate numerical relationships and help students solve various numbers and problems a little more easily.Ī strip diagram is essentially a rectangular bar or box that can be divided up in different ways to represent known and unknown quantities.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
